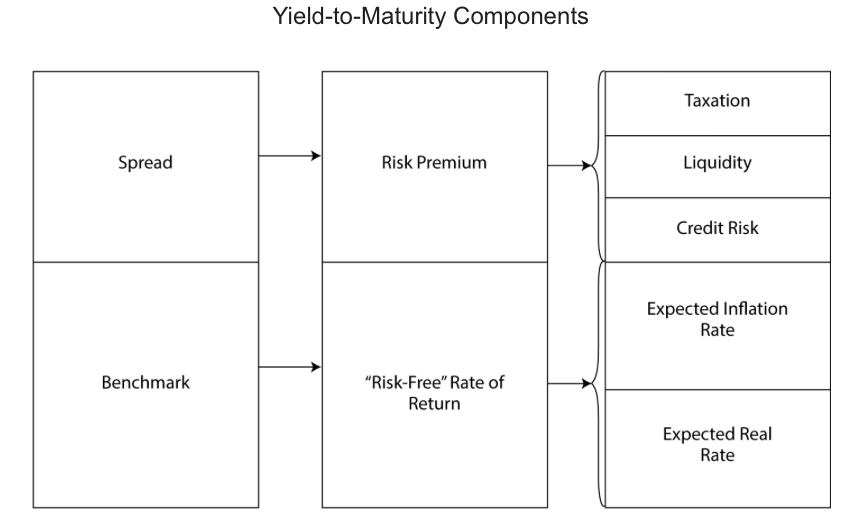
In fixed-income security analysis, it is important to understand why bond prices and yields-to-maturity change. To do this, it is useful to decompose a yield-to-maturity into a base rate or benchmark and an issuer-specific spread.
The yield spread is the difference between the yield-to-maturity and the benchmark yield.
Yield Spreads over the Benchmark Yield Curve
The Z-spread over the benchmark spot curve can be calculated with:
The Z-spread is also used to calculate the option-adjusted spread (OAS) on a callable bond. The OAS, like the option-adjusted yield, is based on an option-pricing model and an assumption about future interest rate volatility. Then, the value of the embedded call option, which is stated in basis points per year, is subtracted from the yield spread.
OAS = Z-spread – Option value in basis points per year.









