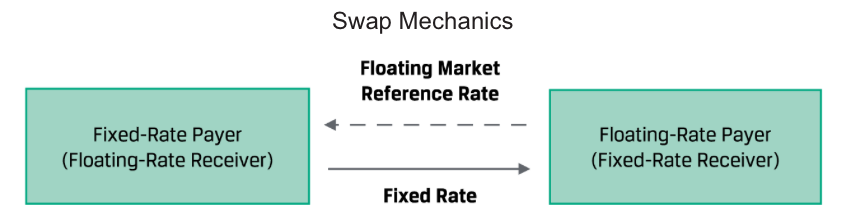
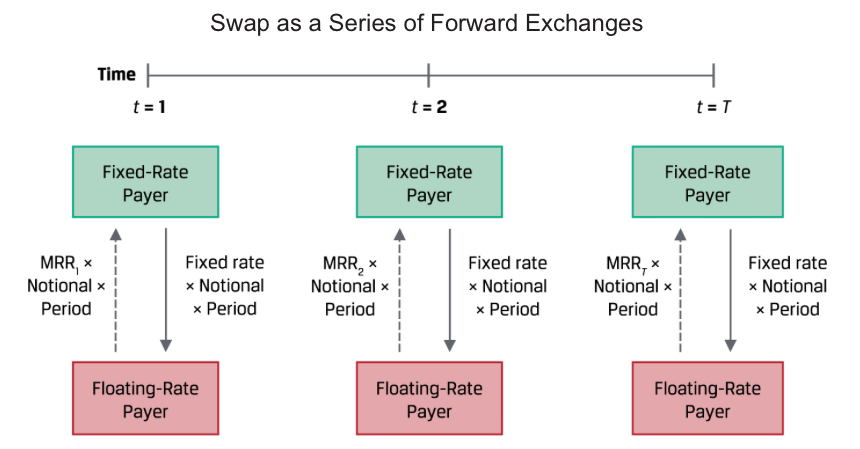
A swap is a firm commitment under which two counterparties exchange a series of cash flows in the future. One set of cash flows is typically variable, or floating, and determined by a market reference rate that resets each period. The other cash flow stream is usually fixed or may vary based on a different underlying asset or rate.
The counterparty paying the variable cash flows as the floating-rate payer (or fixed-rate receiver) and the counterparty paying fixed cash flows as the fixed-rate payer(floating-rate receiver)