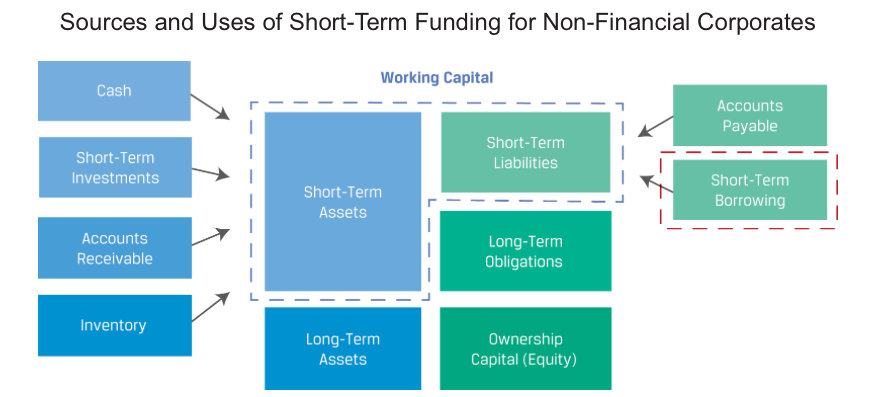
Both non-financial corporations and financial institutions rely on borrowed capital to support their short-term activities.
External Loan Financing
Non-financial corporations often rely on financial intermediaries for short-term financing. Common instruments include
- uncommitted bank lines of credit,
- committed bank lines of credit, and
- revolving credit agreements, or revolvers.
Lines of Credit
Uncommitted lines of credit are the least reliable form of bank borrowing for a company, as the name suggests. A bank offers uncommitted credit lines up to a certain principal amount (“credit line”) for a pre-determined maximum maturity, charging a base or market reference rate (MRR) plus an issuer-specific spread on only the principal outstanding for the period of use.
Committed (regular) lines of credit are a more reliable source of financing than uncommitted lines because they involve a formal written commitment. Committed lines require more bank capital than uncommitted lines, although commitments of less than a year (usually 364 days) minimise a bank’s capital requirement.
Revolving credit agreements, also referred to as “revolvers” (or “operating lines of credit”), are the most reliable source of short-term bank funding.
Secured Loans and Factoring
Secured loans, also called asset-based loans, are loans in which the lender requires the company to provide collateral in the form of an asset, such as a fixed asset that the company owns or high-quality receivables, inventory, or marketable securities. These assets are pledged against the loan, and the lender files a security interest (or right to possess the asset until the loan is repaid) against them.
External, Security-Based Financing
For some firms, loans can be more expensive than debt, secured or unsecured, issued in financial markets. Large, highly rated companies can issue short-term, unsecured notes known as commercial paper (CP) in the public market or via a private placement. Commercial paper issued by corporations typically matures in less than three months and can be used to fund working capital, seasonal demand for cash, or to provide bridge financing (i.e., interim financing that provides funds until permanent financing can be arranged).
Short-Term Funding Alternatives for Financial Institutions
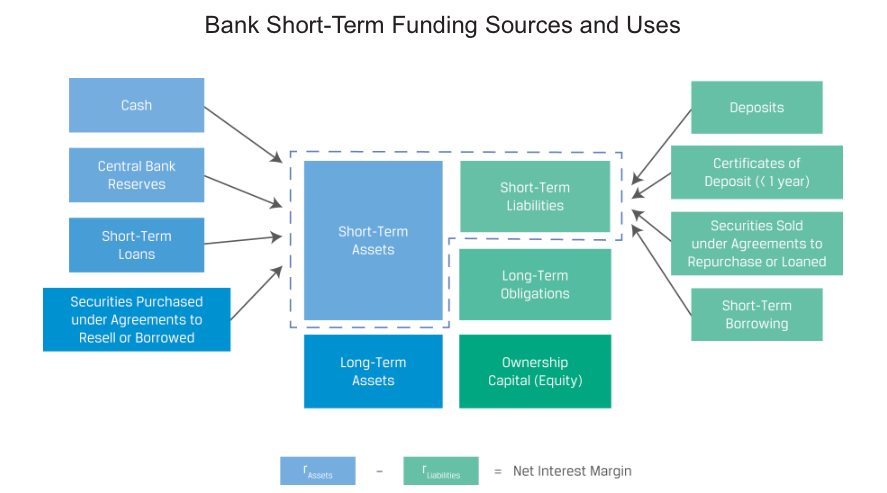
Deposits
Interbank Market
Commercial Paper









