Operating Costs and Their Classification
Generally, operating costs are incurred in generating—or are otherwise related to—current period revenue: all costs related to the acquisition, production, sale, improvement, and delivery of goods and services; the management of business activities; and compliance with laws and regulations.
Behaviour with Output: Fixed and Variable Costs
Using a fixed/variable operating cost classification, operating profit is defined in:
Operating profit = [Q × (P −VC)] − FC1
- Q = units of outputs sold in a period.
- P = price per unit of output.
- VC = variable operating costs expressed per unit of output. Examples include merchandise costs for a retailer like Warehouse Club Inc. and materials and direct labour costs for a manufacturer.
- FC = fixed operating costs, which do not change within a given range of output in the short run. Examples include compensation for salaried employees, depreciation and amortisation, software and IT expenses, insurance, and certain utilities costs. FC is stated on a total dollar, not per unit, basis.
(P − VC), or the contribution margin, must be positive and that Q must be high enough such that FC is exceeded.
Operating leverage can be measured and compared across firms by using the degree of operating leverage (DOL):
DOL = % Δ Operating Profit/% Δ Sales
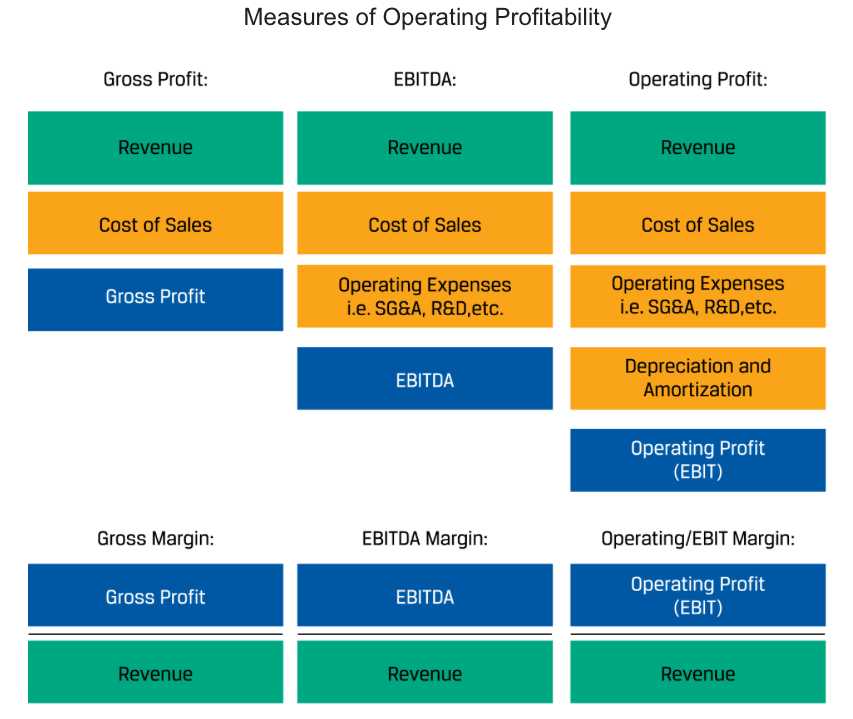
Natural and Functional Operating Cost Classifications and Measures of Operating Profitability