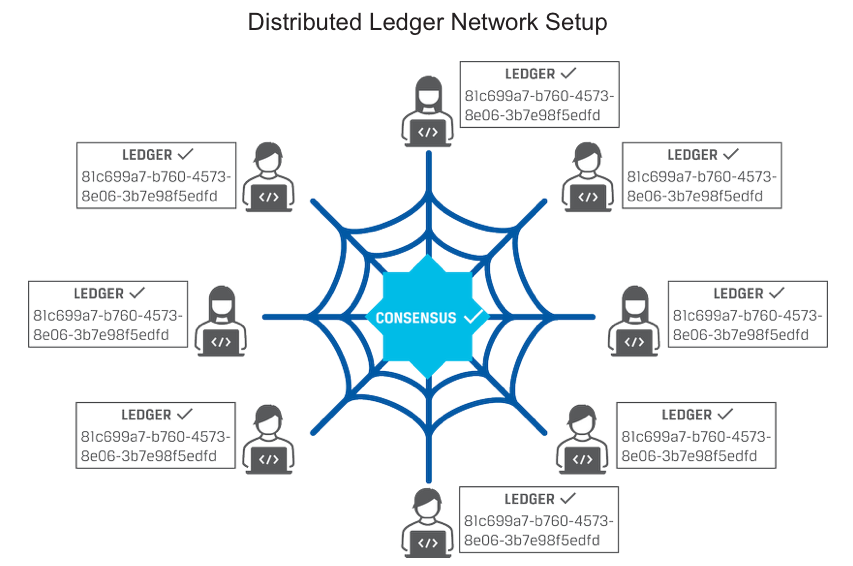
Distributed ledger technology (DLT) based on a distributed ledger (defined later) represents a technological development and offers potential improvements to delivering financing services and financial record keeping.
DLT networks are being considered as a means to create, exchange, and track ownership of financial assets on a peer-to-peer (P2P) basis. Potential benefits of using this technology include greater accuracy, transparency, and security in record keeping; faster transfer of ownership; and P2P interactions.
However, the technology is not fully secure, and breaches in privacy and data protection are possible. Additionally, the computational processes underlying DLT generally require massive amounts of energy to verify transaction activity.
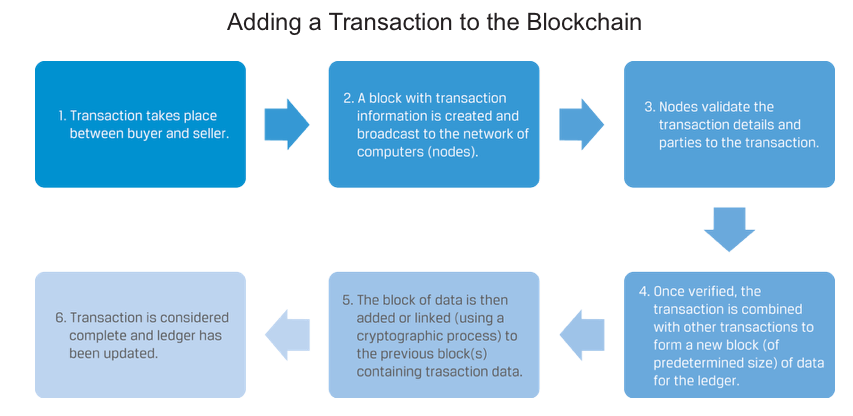
Blockchain is a type of digital ledger in which information, such as changes in ownership, is recorded sequentially within blocks that are then linked or “chained” together and secured using cryptographic methods.
Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake
The Proof of Work (PoW) Protocol
The Proof of Stake (PoS) Protocol
Permissioned and Permissionless Networks
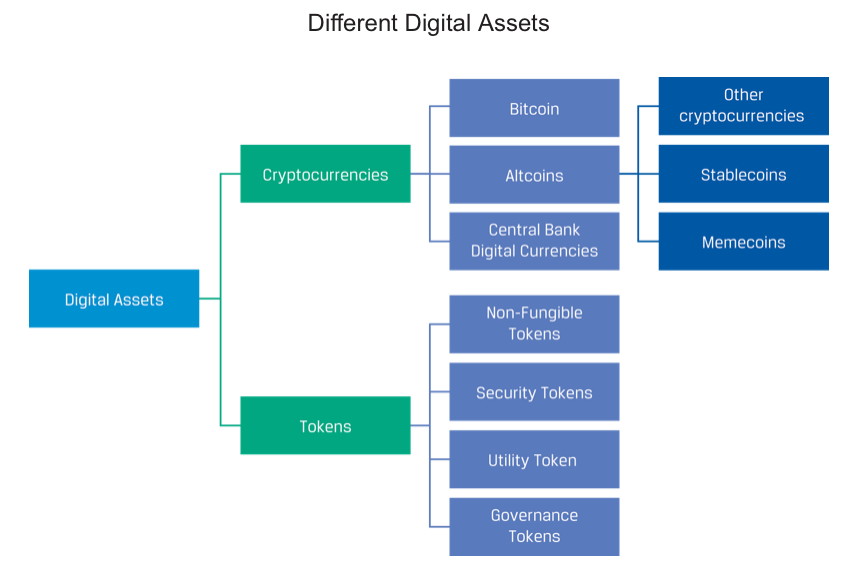
Types of Digital Assets